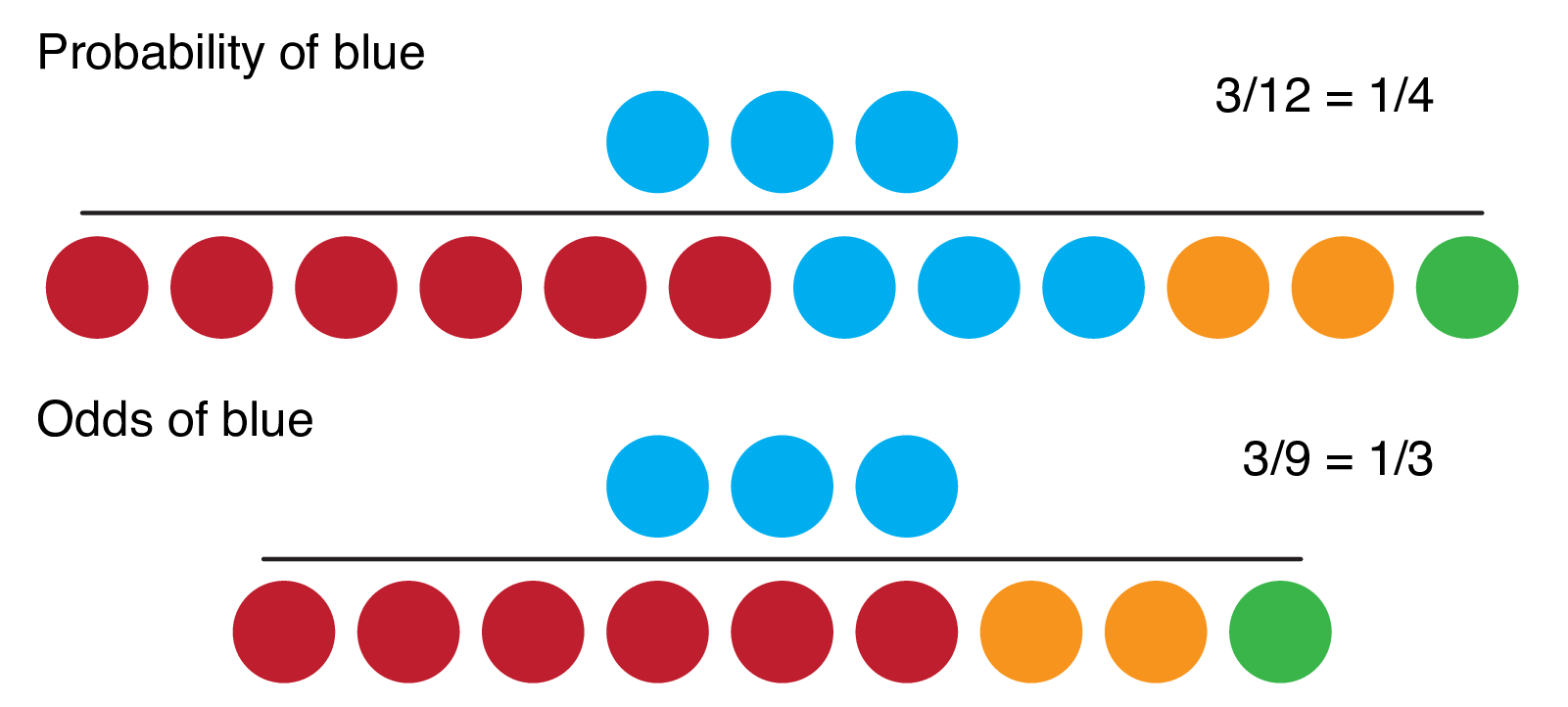
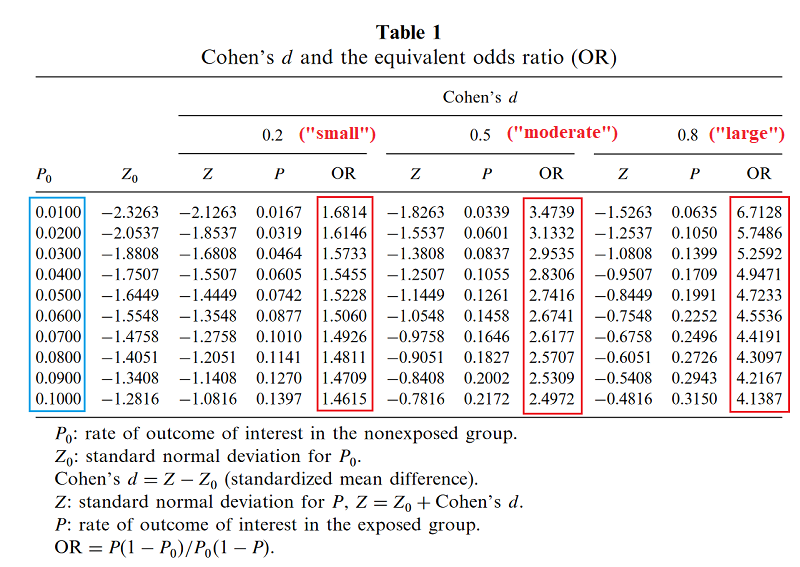
Value As a verb rate is to assign or be assigned a particular rank or level or rate can be to berate, scold The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds ODDS RATIO Odds Ratio = Odds of Event A / Odds of Event B For example, we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball The probability of picking a red ball is 4/5 = 08 The odds of picking a red ball are (08) / 1(08) = 08 / 02 = 4 The odds ratio for picking a redOdds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatment
Odds Ratio Wikiwand
Odds and odds ratio
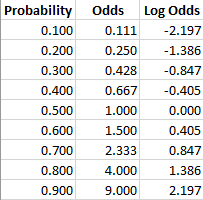
Odds and odds ratio- Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 againstFor example, the odds ratio in an intervention area (baseline73/463 vs followup 46/478) was 061 (95%CI ) and that in a control area (baseline35/303 vs followup 56/333) was 146




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney
An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of X The difference between cats and dogs is 3 percentage points or 3 49 ≈ 612 % increase in probability for dogs over cats Meanwhile the odds ratio is 052 1 − 052 049 1 − 049 ≈ 1128 However I am finding a lot of social science literature intpreting O R − 1 as equivalent to increase in probability ExamplePortantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) And it is this fact that enables us, most of the time, to approximate the relative risk with the odds ratio Table 5 below illustrates the relationship between RR and OR for some probabilities of the outcome
(5) At concentrations below the respective median for each variable, odds ratios of between 142 and 167 were calculated whereas at concentrations above the respective medians the odds ratios ranged from 450 to 633 (P less than 0001) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk (or odds) between the groups being compared The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program
Odds (kansverhouding) is een aan het Engels ontleende term die vooral bij weddenschappen gehanteerd wordt om de kans op een gebeurtenis of uitspraak aan te geven Men spreekt van de odds voor en ook van de odds tegenDe odds voor een gebeurtenis is de verhouding van de kansen dat de gebeurtenis plaatsvindt en dat de gebeurtenis niet plaatsvindt Odds can have any value from zero to infinity and they represent a ratio of desired outcomes versus the field Odds are a ratio, and can be given in two different ways 'odds in favor' and 'odds against' 'Odds in favor' are odds describing the if an event will occur, while 'odds against' will describe if an event will not occur Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
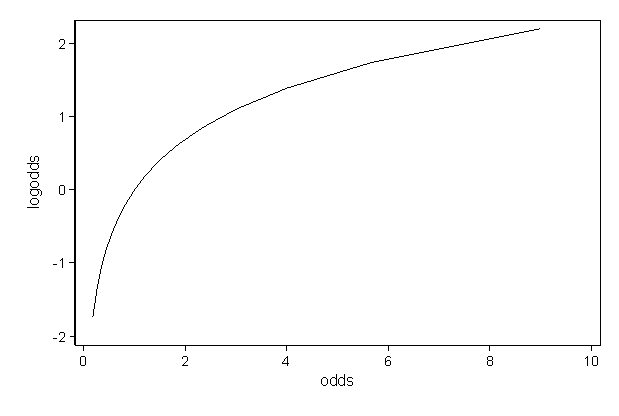
Odds Ratios and Log(Odds Ratios) are like RSquared they describe a relationship between two things And just like RSquared, you need to determine if thisUsing the odds we calculated above for males, we can confirm this log(23) = 147 The coefficient for female is the log of odds ratio between the female group and male group log(1809) = 593 So we can get the odds ratio by exponentiating the coefficient for femaleOdds ratios and logistic regression When a logistic regression is calculated, the regression coefficient (b1) is the estimated increase in the log odds of the outcome per unit increase in the value of the exposure In other words, the exponential function of the regression coefficient (e b1) is the odds ratio associated with a oneunit increase in the exposure



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler
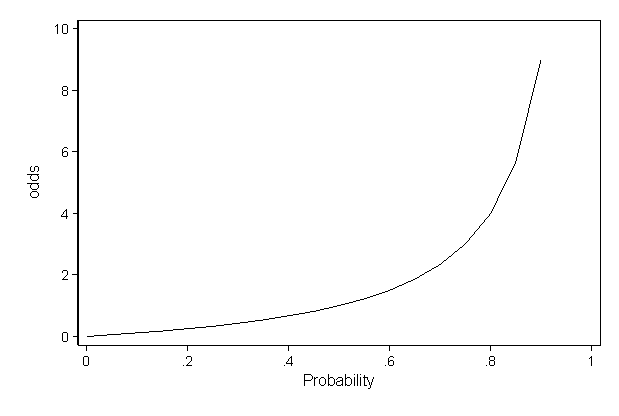
While the odds ratio bypass the interpretation of hard to understand Logits and the odds ratio may be easier to interpret, their meaning is often not easy to understand We can overcome this problem by presenting representative values and its predicted probabilites by the logistic model, since probabilites are easier to understand than odds ratios Probability vs Odds Real life is full of incidents with uncertainty The terms probability and odds measure one's belief in the occurrence of a future event It may confuse since both 'Odds' and 'probability' are related to the potential that event occurs However, there is a difference Probability is a broader mathematical conceptOdds as a ratio (eg 43) Results Probability vs Odds Any chance can be numerically described as either odds or probabilities In the majority of circumstances, neither is preferable to the other The majority of scientists generally refer to probabilities, not odds,



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Ratio Pot Odds / Ratio It is not just number from percentage but it is upside down pot size amount you have to call pot was $80 and they bet $ $100 pot and call $ = 5 1 You are risking $1 to win $5 Now the pot is $1 Hand Odds (cards left outs)/outs If you have 8 outs on the turn then (468)/8 = 475 1 or (1 fraction Crude Odds Ratio – the odds ratio calculated using just the odds of an outcome in the intervention arm divided by the odds of an outcome in the control arm Adjusted Odds Ratio – is the crude odds ratio produced by a regression model which has been modified (adjusted) to take into account other data in the model that could be for instance a prognostic baseline variableEnglishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not , however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when results are reported refers to the ratio of two odds or, if you prefer, the ratio of two odds ratios That is, let us write




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
If odds ratio is 25, then there is a 25 times higher likelihood of having the outcome compared to the comparison group Here the odds ratio would be 080 The odds ratio also shows the strength of the association betweenRather the odds is threefold greater The odds ratio provides a measure of the association between treatment (intervention compared with control) and the primary outcome The unadjusted odds ratio was derived as the odds of a gain of 15 letters or more of visual acuity at one year for the intervention divided by the odds for the control treatment (21/44)÷ (2/64)= (21/44)× (64/2




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
Odds ratio and relative riskDie OddsRatio (Quotenverhältnis oder Chancenverhältnis) wäre dann 0,28 / 0,16 = 1,75 Ein Wert größer 1 heißt, dass die Quote in der ersten Gruppe größer ist, ein Wert kleiner 1, dass die Odds der ersten Gruppe kleiner sind Ein Wert von 1 ist ein gleiches Quotenverhältnis(12) Matchedpair analysis yielded an odds ratio of 70 with a 95% confidence interval of 17 to 28 (13) When the 2 preinvasive disease categories were combined, an elevated odds ratio of borderline significance was found for 2 of the 3 lower quintiles for the 4 low quintiles combined



1



1
As nouns the difference between odds and rate is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while rate is (obsolete) the estimated worth of something; Summary Our theoretical Odds Ratio is 0319 with a CI(0, 041), which is close to the true Odds ratio, 03This indicates if the undergraduate students are from the school in prestige 3 or 4, the chances of them getting in graduate school is 38% that of the students from prestige 1 or 2 undergraduate schools What does an odds ratio of 25 mean?




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
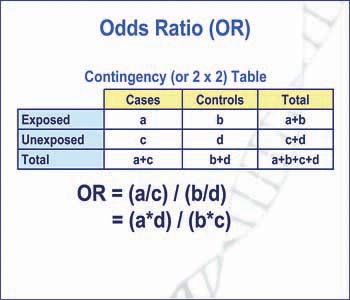
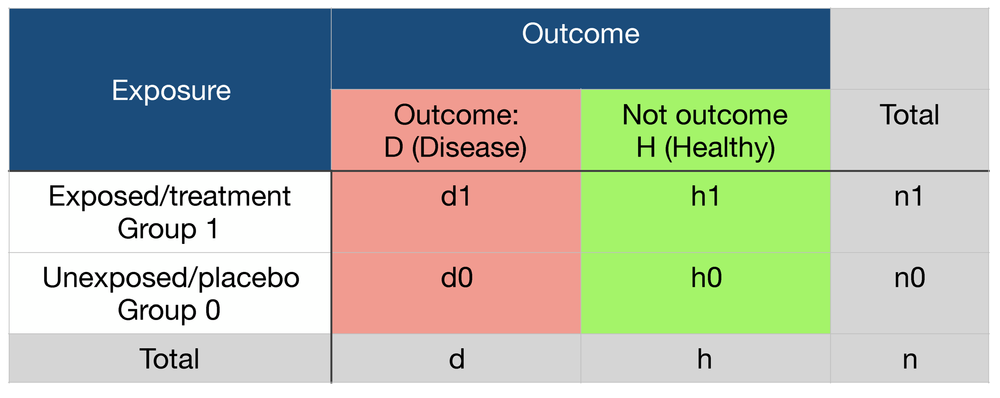
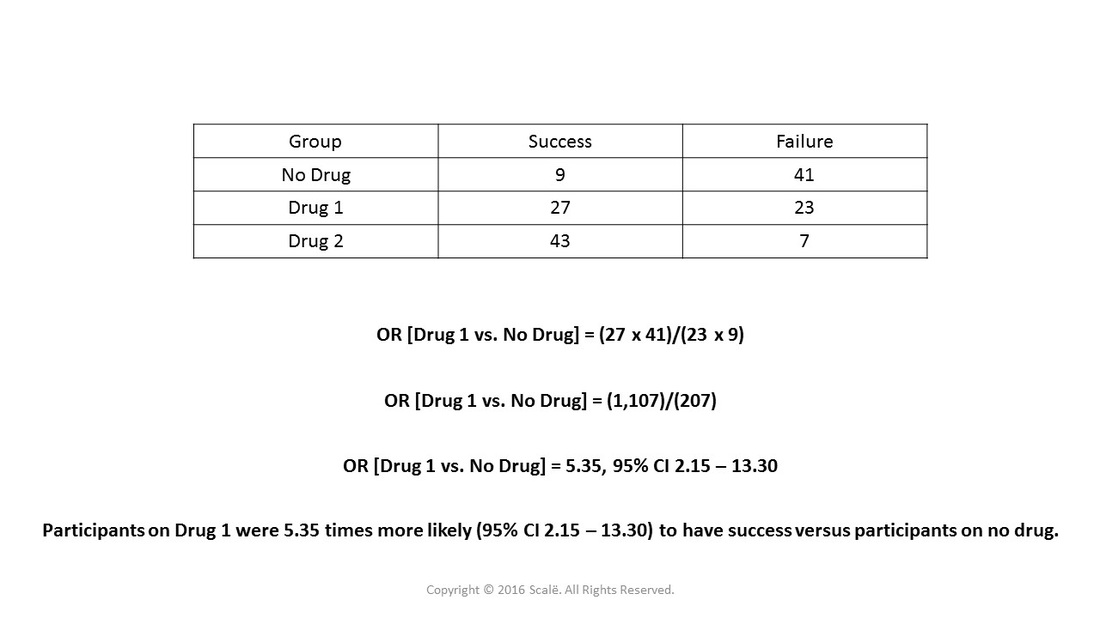
Dan is de odds 1 tegen 19 (5,3%) Vandaar dat de odds ratio als benadering van het relatief risico alleen mag gebruikt worden wanneer het risico op de uitkomst klein is (Odds Ratio (OR) is a measure of association between exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure In rare outcomes OR = RR (RR = Relative Risk) This applies when the incidence of the disease is < 10%The odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived From the data in the table 1, it is calculated as follows OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (152/17)/



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
marginal effects vs odds ratios , 1854 Hello, I am currently trying to understand the pros and cons of using odds ratios vs marginal effects for the interpretation of a multinomial logit If anyone could enlighten me, or point me to a resource that could help with this decision, it would be greatly appreciatedWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR Odds ratio and risk ratio are related concepts that can be interchanged when the prevalence of the effect is low, but not in other situations The realm of science is full of traps They're everywhere Neither the major medical journal, nor the most prestigious authors are free of them Many people tend to take advantage of our ignorance and




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Plotting Odds Ratio Vs Continuous Variable In Stata Stack Overflow
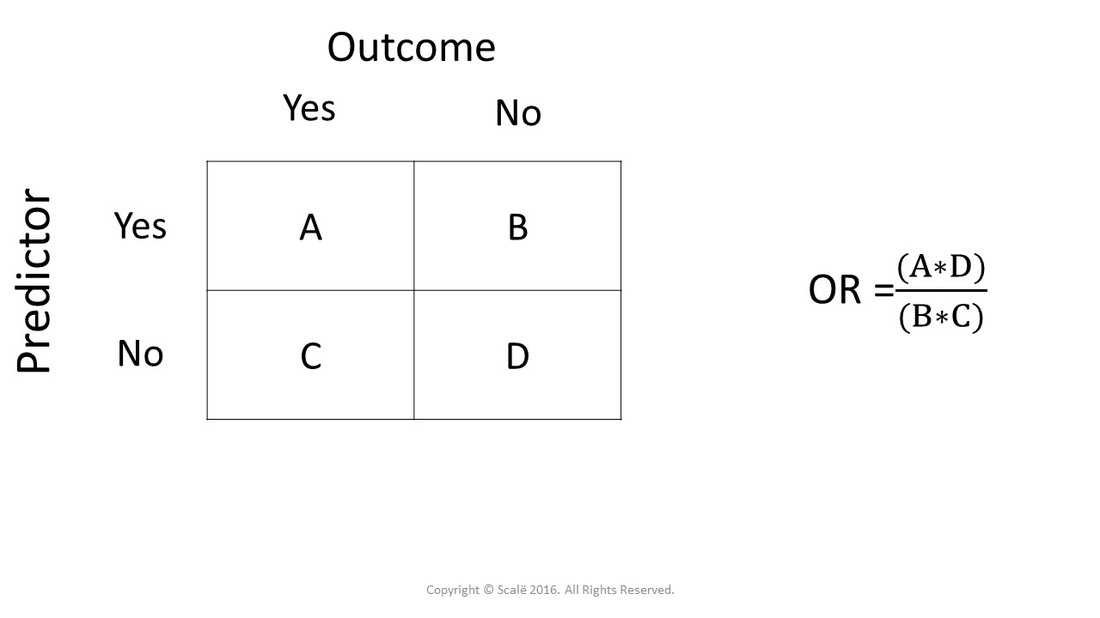
Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold; The primary difference between odds and probability is that while odds is a ratio of occurrence to nonoccurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the whole Odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or in decimal




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




Diagnostic Odds Ratio Wikipedia
The adjusted odds ratio for daycare attendance before 1 year of age was 059 (95% CI 040, 087) Results were similar with persistent cases Among transient casesThe odds ratio An odds ratio (OR) is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome In a casecontrol study you can compare the odds that those with a disease will have been exposed to the risk factor, with the odds that those who don't have the disease or condition will have been exposedOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a r



Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
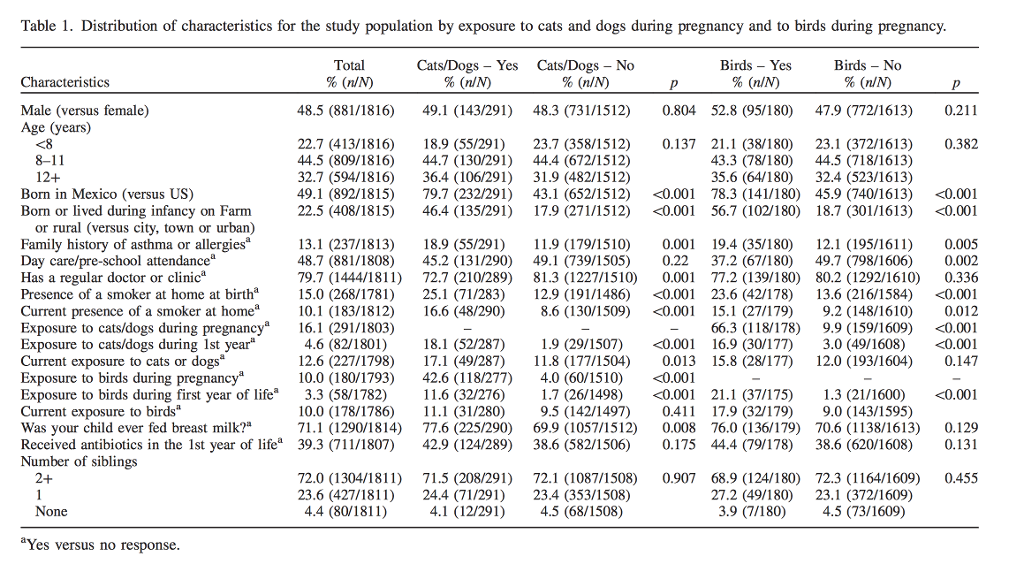



Calculating Odds Ratio Using Table 1 Calculate Chegg Com




What Are Cross Tables Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Gcp Service



Risk




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Strategies For Graphing Distributions Of Log Odds Estimates And The Corresponding Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
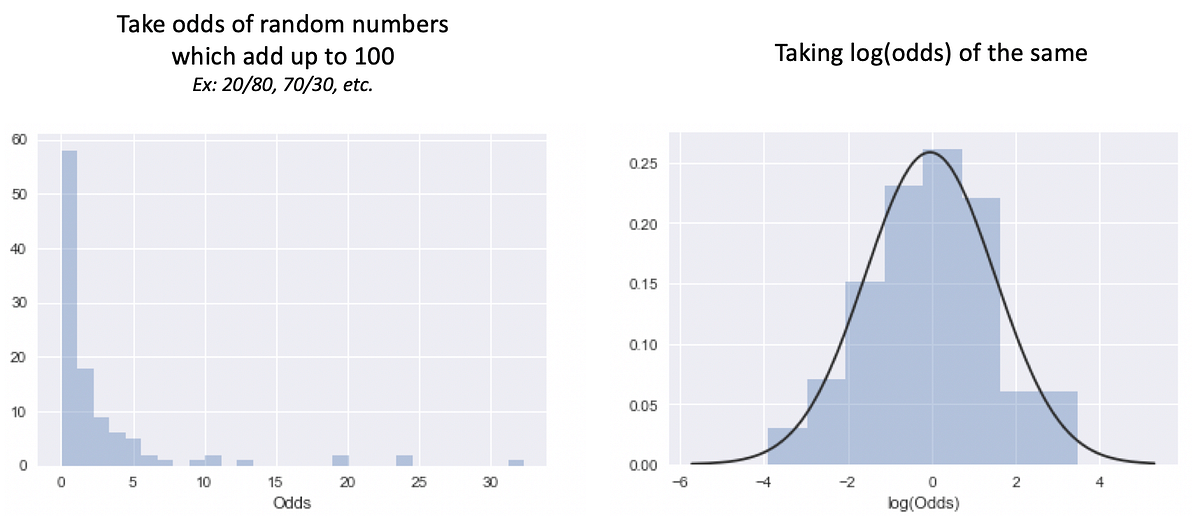



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney



Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World



Logistic Regression Odds Ratio



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
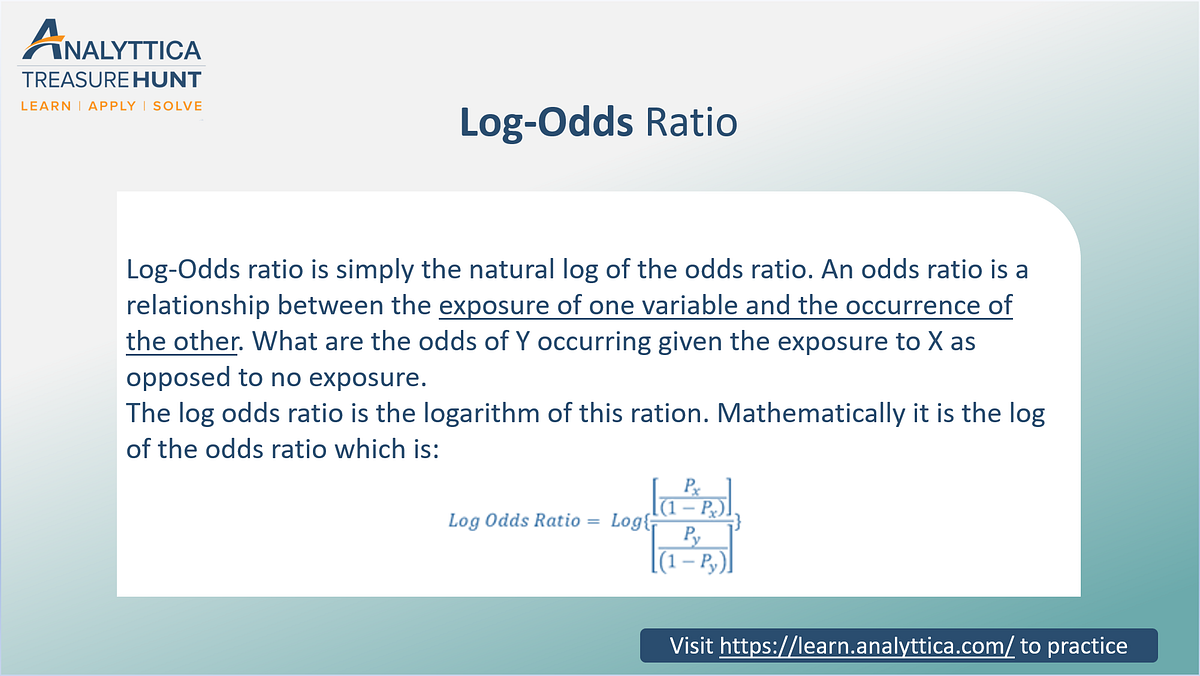



Log Odds Ratio Analytics Function Series By Analyttica Datalab Medium



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss




Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology




Odds Ratio Article
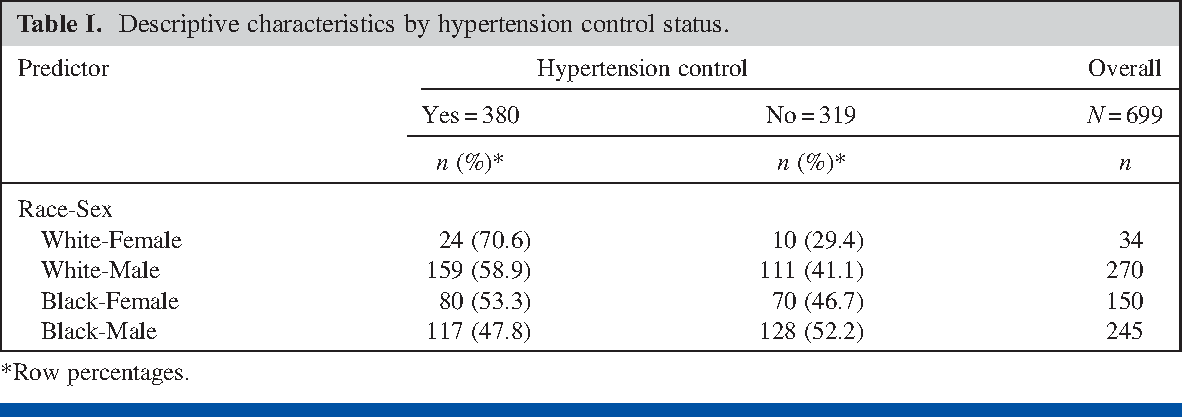



Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Odds Ratio Wikiwand




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Understanding Odds Ratio In Medical Risk Analysis




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube Case Control Study Study Research Methods



Never Tell Me The Odds Ratio Slate Star Codex



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



27 Sep 01 Draft




How To Get Odds Ratio In Ordinal Logistic Regression Jmp User Community




The Effect Of A Lack Of Dose Response Results On Odds Ratio Cross Validated



What Is A Pooled Odds Ratio Quora




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To




Adjusted Odds Ratio Definition Examples Statology




Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium




Diagnostic Odds Ratio Core Im Podcast




Figure 7 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Younger And Older Subgroups Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Newbedev




Figure 6 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Women And Men Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For Primary



Graph Of Odds Ratio Versus Sle Image Eurekalert Science News Releases




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Cohort Specific And Meta Analysis Pooled Odds Ratios Ors Of Download Scientific Diagram




Crude Odds Ratios Cor And Adjusted Odds Ratio Aor And Their 95 Download Table




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Meta Analysis Odds Ratio



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Probability Odds Odds Ratio Youtube
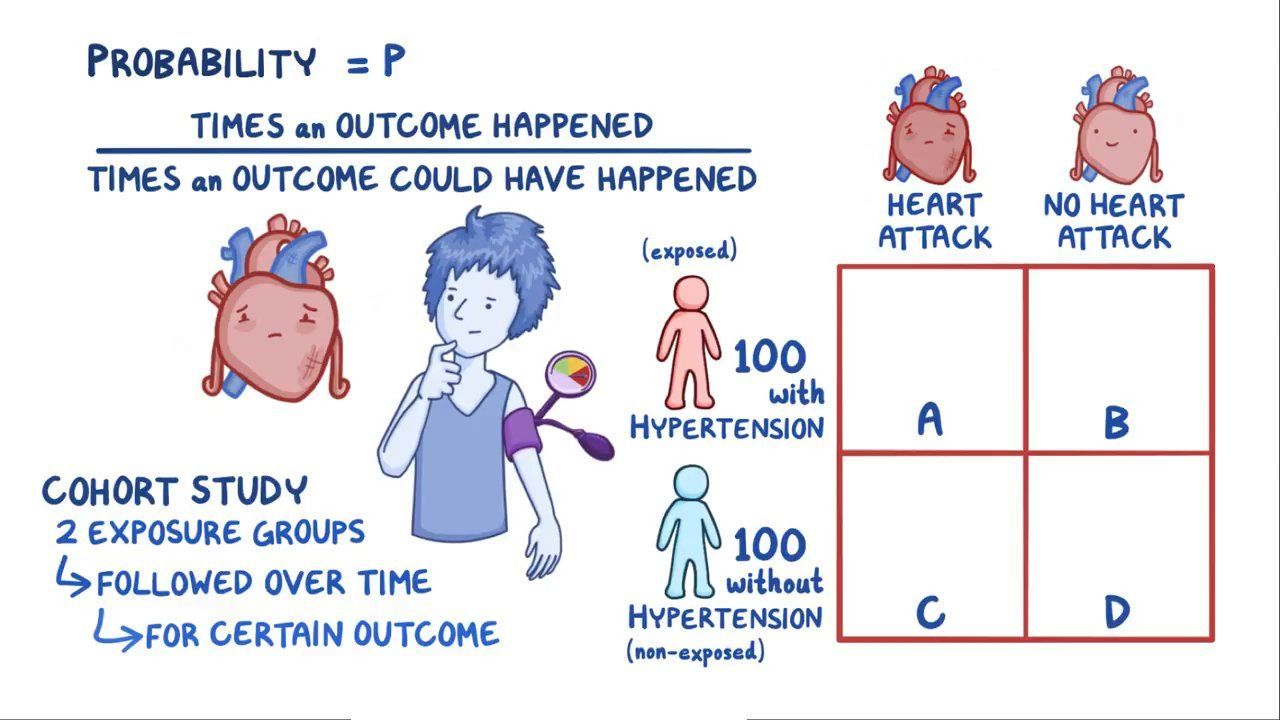



Odds Ratio Osmosis
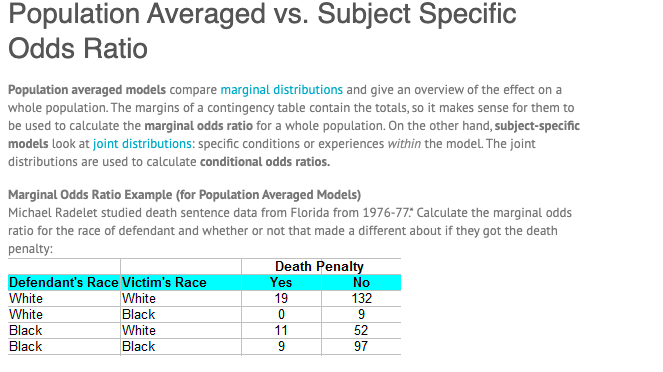



Population Averaged Vs Subject Specific Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Solved How Do I Get The Odds Ratio In Fisher Exact Test Sas Support Communities
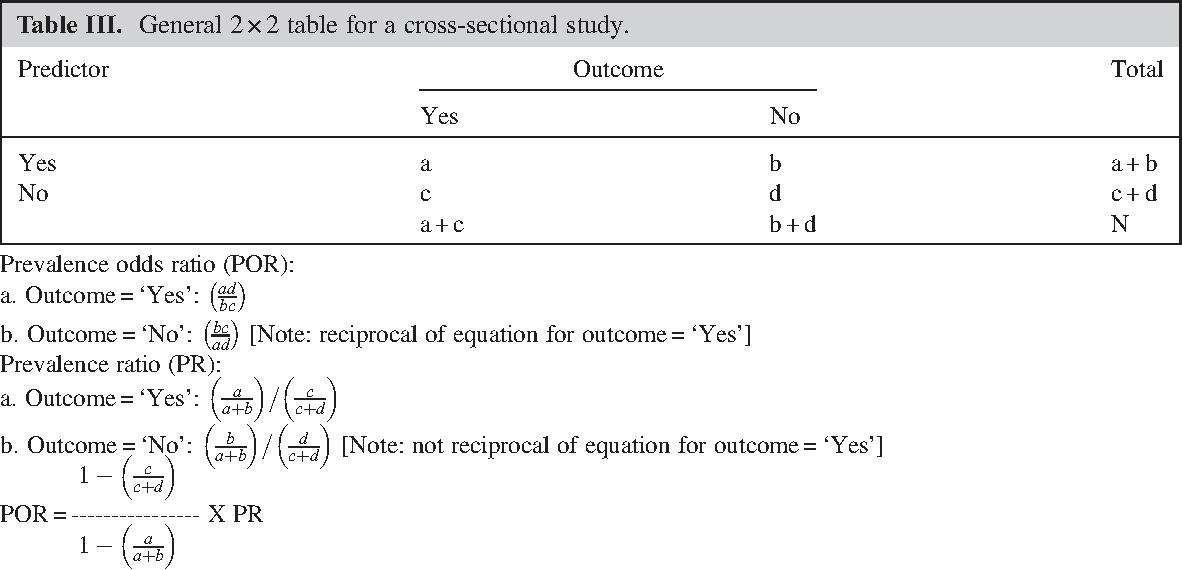



Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



The Difference Between Probability And Odds




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
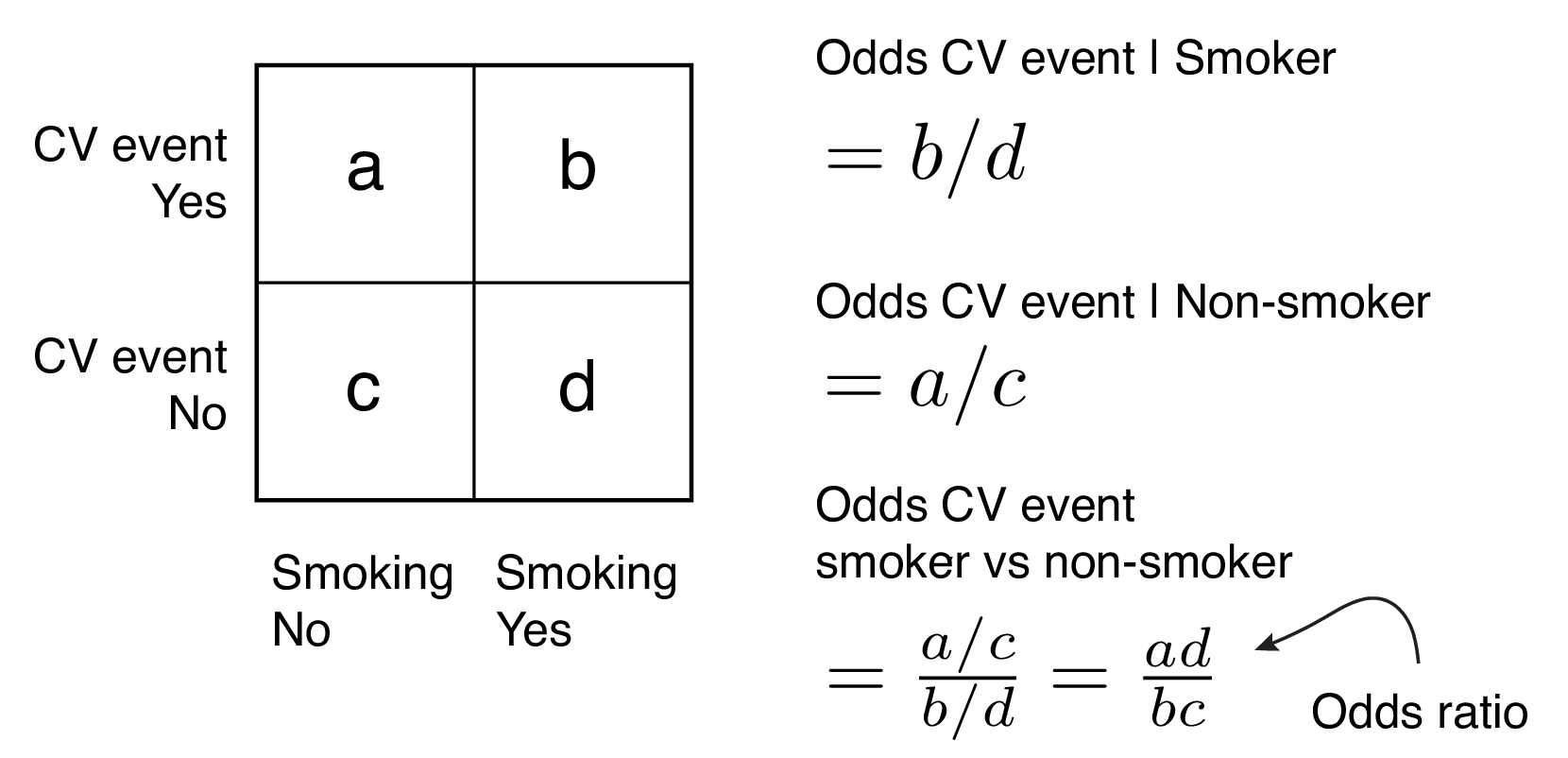



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science



Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Likelihood Ratio And Odds Ratio Slope Values Represent Odds As Shown Download Scientific Diagram



Hazard



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream
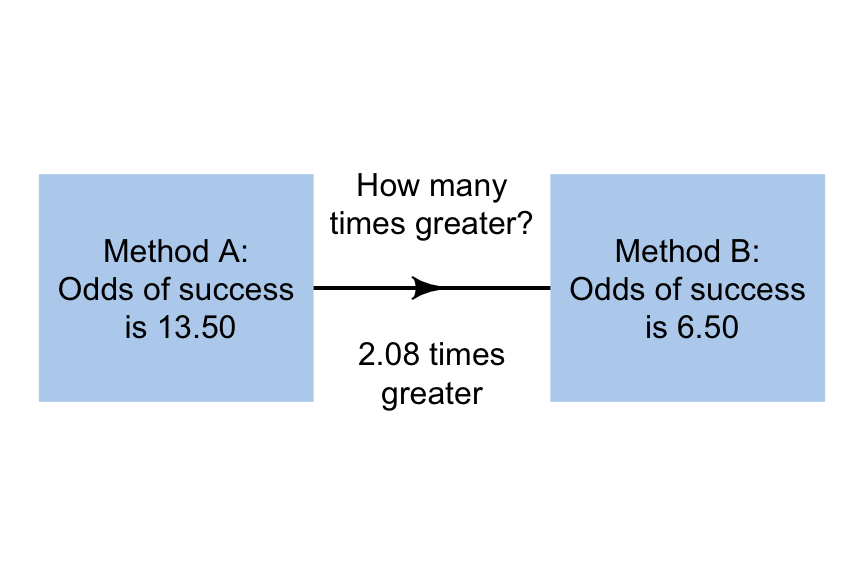



14 3 Odds Ratios Scientific Research And Methodology




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



No comments:
Post a Comment